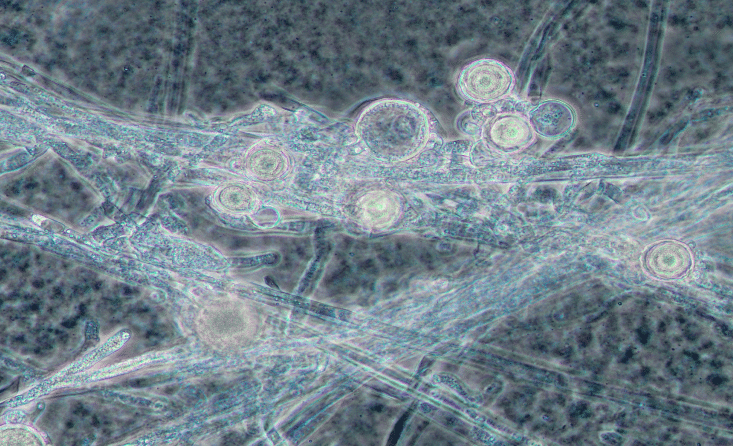
Root rot in pea is caused by a complex of four different pathogens, one being aphanomyces.
Aphanomyces euteiches is a newer pathogen in the Prairie regions, but likely the most damaging for pea, and this year we are detecting it in around nearly 80 per cent of samples we receive.
Aphanomyces is a water mold — it prefers water-logged soil. It was first confirmed in Saskatchewan in 2012 and Alberta in 2013. It produces oospores which have double thick-walled cells. Symptoms of root rot caused by Aphanomyces euteiches in pulses are:
- Stunting
- Yellowing
- Poor root growth
- Little nodulation
- Browning of root area; caramelized roots are classic signs of aphanomyces infection
What tests are available?
There are various testing options available for aphanomyces detection:
- Pulse root rot test — Plant samples are submitted with roots intact. Root tissue is analyzed visually, microscopically and later plated to report the presence of four root rot-causing pathogens. It is a seven-day test with quantitative results.
- Aphanomyces DNA test for plant tissue — Infected plants are concentrated sources of the pathogen and represent a significant escalation in the amount of inoculum present in a field. Scout for suspect plants and submit fresh, frozen or dried roots for testing. The results are released in 48 hours and will give a Yes/No answer. It is challenging to culture Aphanomyces euteiches on plates and it is recommended to get a DNA test.
- Aphanomyces DNA test for soil — For field soil, collect the top five to 10 cm of A-horizon, or less as depth allows, without taking any B-horizon. Collect in a W-shaped pattern at entrances to the field and other suspect spots (like low-lying areas, gardens, well/utility sites, soil clumps at entrances). Submit a two-cup sample. You can submit individual samples or mix multiple samples well and submit a composite sample. Air dry the sample prior to submission to the lab and submit sample in a sealed plastic freezer bag.
- Seed Test — Aphanomyces root rot is not generally seedborne; if a seed sample is submitted, the soil attached to the seed is tested, not the seed itself. Seeds can be tested using DNA testing method for aphanomyces detection. A germination and vigour test along with an aphanomyces DNA test will give a full profile of the sample. Ensure you get germination and vigour tests on your seed and only plant seed with the highest rates because seed with low vigour is more susceptible to Aphanomyces infection.